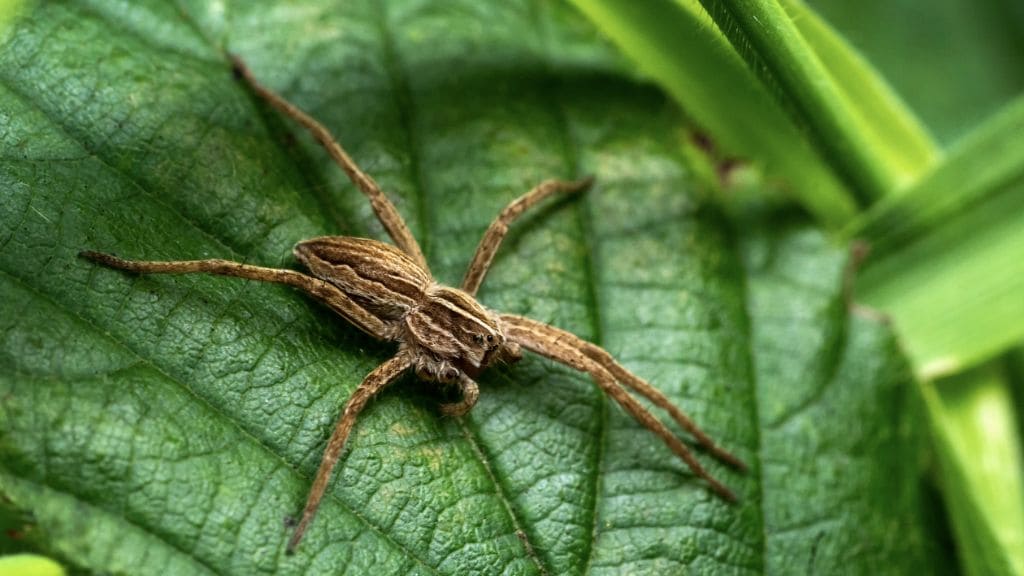
Wolf spiders, with their hairy bodies and swift movements, often evoke a mix of curiosity and caution among those who encounter them. Found across diverse habitats worldwide, these arachnids play a vital role in controlling insect populations, making them beneficial predators in ecosystems. Despite their intimidating appearance, understanding their behavior and interactions with humans reveals that they pose minimal threat. This article delves into the myths surrounding wolf spiders, clarifies their venomous nature, and provides practical insights into managing encounters with these fascinating creatures.
In recent years, misconceptions about wolf spiders’ toxicity have led to concerns among homeowners and outdoor enthusiasts. Contrary to popular belief, wolf spiders are not aggressive towards humans and only bite defensively when threatened. Their venom, while effective against small prey, poses little risk to human health. This guide aims to dispel fears and foster a deeper appreciation for the ecological roles played by wolf spiders, emphasizing non-lethal approaches to coexist peacefully with these natural pest controllers.
By exploring the facts behind wolf spiders’ behaviors and debunking common myths, individuals can adopt informed strategies for managing encounters. From understanding their distinctive hunting techniques to practical tips on preventing entry into homes, this article empowers readers to appreciate the presence of wolf spiders in their environment while ensuring personal comfort and safety. Whether encountered indoors or outdoors, learning about wolf spiders enriches our understanding of biodiversity and promotes sustainable practices in pest management.
Introduction to Wolf Spiders
Wolf spiders, members of the family Lycosidae, are a diverse and widespread group of arachnids known for their robust build, hairy bodies, and agile hunting behavior. Unlike many of their spider relatives that rely on stationary webs to capture prey, wolf spiders are adept predators that actively stalk and ambush their victims. This unique hunting strategy has earned them their name, drawing parallels to the stealthy tactics employed by wolves in pursuit of their prey.
Diversity and Distribution
The family Lycosidae encompasses over 2000 species distributed across various habitats worldwide. From temperate forests to arid deserts and tropical rainforests, wolf spiders have adapted to thrive in diverse environmental conditions. Their ability to inhabit both natural landscapes and human-altered environments underscores their ecological versatility and resilience.
Physical Adaptations
Physically, wolf spiders are characterized by their large size compared to many other spider species. Their bodies, often covered in dense hair, serve multiple functions, including sensory perception and insulation. Their eight eyes, arranged in three distinct rows, provide exceptional vision, crucial for locating and tracking prey during nocturnal forays.
Habitat and Behavior
Wolf spiders are primarily ground-dwelling creatures, seeking shelter in burrows or under rocks, logs, and leaf litter during the day. Unlike web-building spiders, they rely on their formidable agility and keen senses to pursue insects, small vertebrates, and other spiders on the ground or in low vegetation. This hunting behavior not only distinguishes them from their relatives but also highlights their role as active predators in terrestrial ecosystems.
Reproductive Strategies
Reproduction in wolf spiders involves courtship rituals where males engage in intricate displays to attract females. After mating, females produce egg sacs, which they carry attached to their spinnerets until the spiderlings hatch. This maternal care is uncommon among spiders and reflects the investment females make in ensuring the survival of their offspring in often-challenging environments.
Interactions with Humans
Despite their beneficial role in controlling pest populations, wolf spiders often provoke fear and anxiety when encountered indoors or in close proximity to human habitation. Their intimidating appearance, coupled with misconceptions about their potential danger, has contributed to their undeserved reputation as harmful creatures. Understanding their natural history and behavior can alleviate unnecessary concerns and foster appreciation for their ecological significance.
Dispelling Myths: Are Wolf Spiders Poisonous?
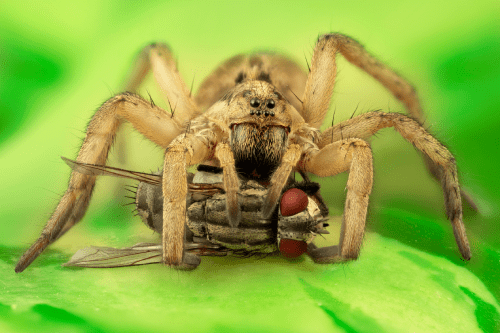
One of the enduring myths surrounding wolf spiders revolves around their perceived toxicity to humans. It is crucial to clarify that wolf spiders, like the vast majority of spiders, are venomous but not poisonous. This distinction is essential in understanding their potential impact on human health. Venomous organisms inject toxins into their prey or defensive bite, typically through specialized appendages such as fangs. In contrast, poisonous organisms pose harm through ingestion or contact, such as certain plants or toxins that seep through skin.
Understanding Wolf Spider Venom
The venom of wolf spiders serves primarily as a tool for subduing prey rather than as a defense mechanism against larger predators like humans. While their venom is potent enough to immobilize insects and small animals, it lacks the complexity and potency found in venomous spiders that pose a significant threat to humans, such as black widows or recluse spiders.
Myth vs. Reality: Bites and Human Health
Contrary to popular belief, wolf spiders are not aggressive towards humans and typically avoid confrontation. Bites occur infrequently and are usually a defensive response when the spider feels threatened or inadvertently handled. When a bite does occur, the immediate effects may include localized pain, redness, and swelling, similar to a bee sting. These symptoms generally subside within a few days with basic first aid measures and pose minimal risk of long-term health consequences.
Allergic Reactions and Individual Sensitivity
While most people experience mild reactions to wolf spider bites, such as temporary discomfort and irritation, allergic individuals may exhibit more pronounced symptoms. Severe allergic reactions to spider venom are rare but can include generalized itching, swelling, or respiratory distress. Individuals with known allergies to insect venom should exercise caution and seek medical attention promptly if they suspect an adverse reaction.
Clinical Management of Wolf Spider Bites
Treatment for wolf spider bites focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing infection. Immediate steps include cleaning the bite area with soap and water, applying a cold compress to reduce swelling, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers as needed. It is advisable to monitor the bite site for any signs of infection, such as increased redness or discharge, and seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or persist.
Educating for Coexistence
Dispelling myths about the toxicity of wolf spiders is essential for fostering informed attitudes and practices towards these beneficial creatures. By understanding their role in pest control and their minimal threat to human health, individuals can adopt non-lethal methods to manage encounters, such as safely relocating spiders outdoors rather than resorting to chemical pesticides. Emphasizing education and respect for wildlife encourages coexistence and supports biodiversity conservation efforts in both urban and natural environments.
Managing Encounters with Wolf Spiders
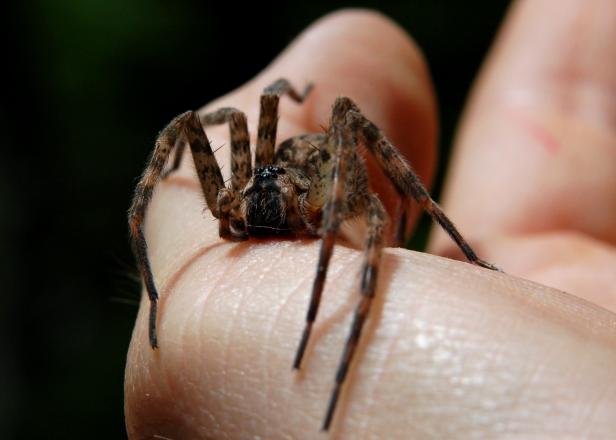

Non-lethal Approaches
When faced with a wolf spider indoors, it’s important to remember that these arachnids play a beneficial role in controlling pest populations. Instead of resorting to lethal measures, such as chemical pesticides that can harm beneficial insects and disrupt ecosystem balance, consider non-lethal methods for managing encounters. Safely capturing and relocating spiders outdoors using a container and paper can help maintain a balance between human comfort and ecological sustainability.
Habitat Modification
Preventative measures can reduce the likelihood of encountering wolf spiders indoors. Sealing cracks, gaps, and entry points around doors and windows minimizes opportunities for spiders to enter buildings. Removing clutter, such as stacked firewood or piles of leaves, from around the perimeter of structures reduces potential harborage sites for spiders and their prey.
Integrated Pest Management
Adopting an integrated pest management (IPM) approach emphasizes proactive strategies to minimize pest populations while minimizing environmental impact. By addressing underlying factors that attract prey species, such as ensuring proper sanitation and reducing excess moisture indoors, homeowners can create less hospitable environments for both pests and their predators, including wolf spiders.
Educating for Understanding
Educational outreach plays a vital role in fostering understanding and appreciation for wolf spiders and their ecological contributions. By dispelling myths and misconceptions about their perceived danger, individuals can develop a more nuanced perspective that encourages coexistence with these beneficial predators. Teaching children and adults alike about the role of spiders in ecosystems promotes respect for biodiversity and encourages responsible stewardship of natural resources.
Professional Assistance
In cases where spider populations become overwhelming or persistent, consulting with pest management professionals trained in wildlife conservation and humane pest control practices can provide tailored solutions. These professionals can offer guidance on effective pest exclusion techniques and recommend environmentally sensitive treatments that prioritize human health and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Wolf Spiders

1. Are wolf spiders dangerous to humans?
Wolf spiders are not generally dangerous to humans. While they possess venom for subduing prey, their bites are rarely harmful to humans and typically result in mild symptoms like localized pain, redness, and swelling. Severe reactions are extremely rare and usually occur only in individuals with allergies to spider venom.
2. Do wolf spiders bite humans?
Yes, wolf spiders can bite humans if provoked or handled roughly. However, they are not aggressive and will typically only bite in self-defense. Encounters with humans often result from accidental contact or if the spider feels threatened.
3. How can I prevent wolf spiders from entering my home?
To prevent wolf spiders from entering your home, seal cracks and gaps around doors, windows, and foundations. Keep indoor spaces clutter-free and remove potential hiding spots like piles of clothing or debris. Regularly clean and vacuum to eliminate prey insects that may attract spiders.
4. What should I do if I find a wolf spider in my house?
If you encounter a wolf spider indoors, the best approach is to gently capture it using a container and paper and release it outdoors. Avoid squashing spiders as this can release venom and may attract other pests. Taking these steps helps maintain a balance between pest management and respecting wildlife.
5. Are wolf spiders beneficial?
Yes, wolf spiders play a beneficial role in ecosystems by controlling populations of insects and other arthropods. They are natural predators of pests like mosquitoes, flies, and cockroaches, contributing to natural pest control without the need for chemical interventions.
Conclusion
The portrayal of wolf spiders as menacing creatures capable of inflicting harm upon humans is largely unfounded. While their formidable appearance and hunting tactics may evoke fear, these spiders pose minimal risk and should be regarded with respect for their ecological contributions. Educating ourselves about their behavior and biology is key to fostering a harmonious relationship between humans and the natural world.

